Sevengill Shark Adomavirus
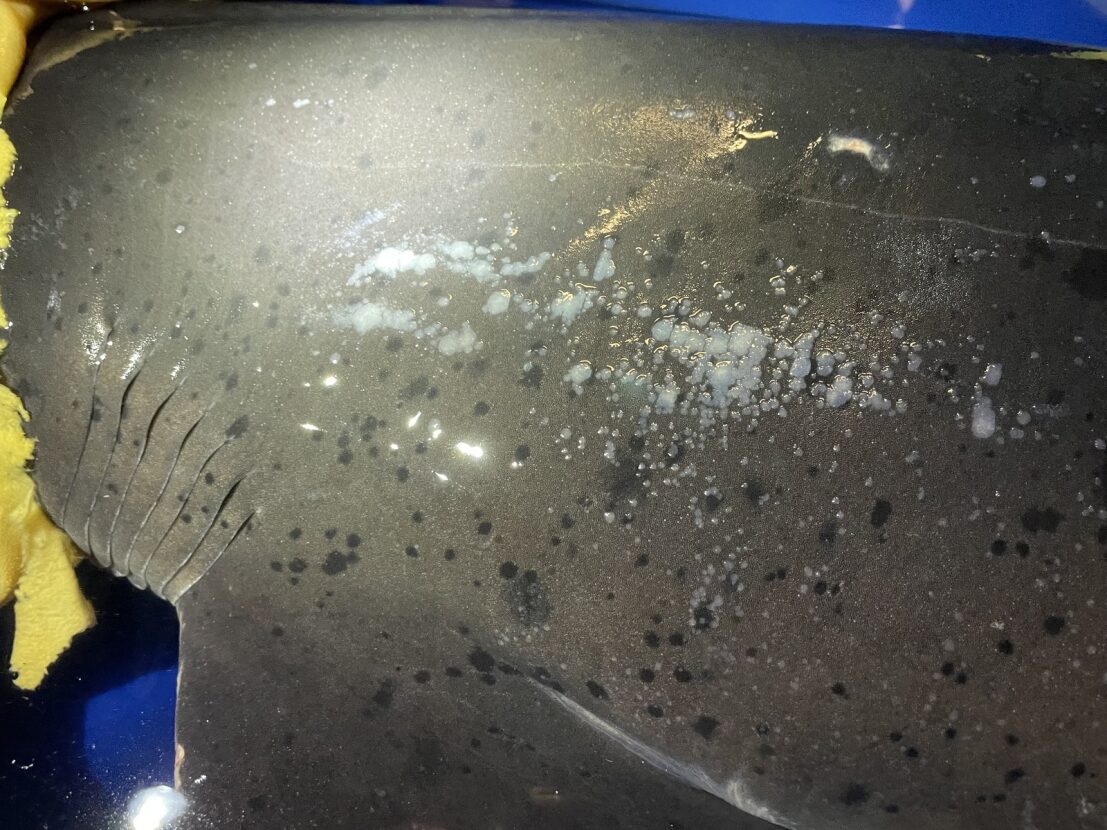

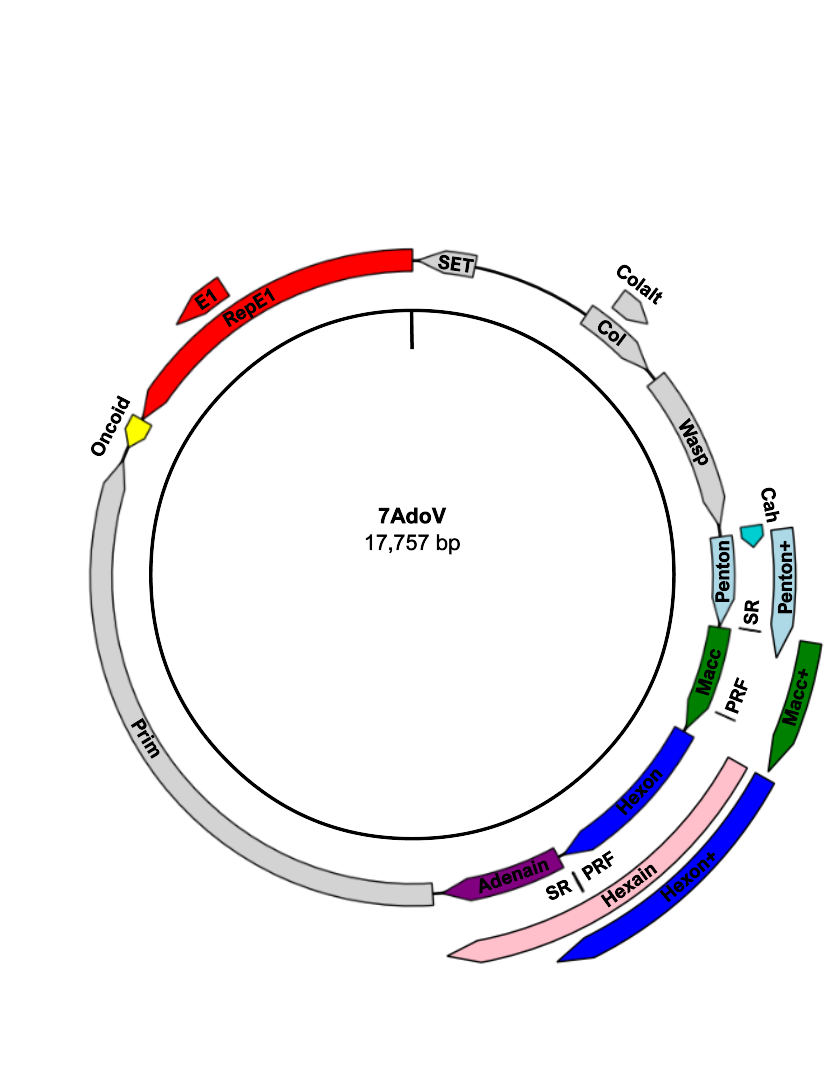
Using metagenomics, we were able to detect a previously unknown adomavirus from a broadnose sevengill shark (Notorynchus cepedianus) presenting with epidermally proliferative skin lesions. A BLAST alignment to the most closely related guitarfish (Rhynchobatus djiddensis) adomavirus allowed for the identification and characterization of the novel alpha-adomavirus, the first of its kind identified in the cow shark family (Hexanchidae).
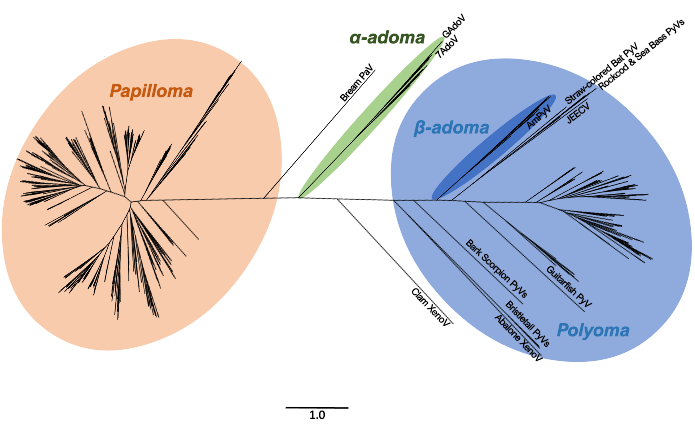
Using a dynamic and thorough molecular virology workflow—including both phylogenetic and functional analyses—we provide insight into a likely long-existing yet recently characterized virus clade, highlighting the further distinction of alpha- (papilloma-replicase-like-encoding) and beta (polyoma-replicase-like-encoding) adomavirus subfamilies.
Genomic, transcriptomic, and in situ data are meshed to match molecular and pathological evidence of epidermal virus proliferation with host response, identifying the broadnose sevengill shark adomavirus as the likely causative agent of the hyperplastic lesions. Structural prediction of 7AdoV capsid proteins reviewals the structure below encoding the hexon gene.